
Rakieta NASA Space Launch System (SLS) i statek kosmiczny Orion z ich europejskim modułem serwisowym docierają na miejsce startu 39B w NASA Kennedy Space Center na Florydzie, USA, 4 listopada 2022 roku. Misja Artemis I będzie pierwszym testem SLS i Orion i Europejska Jednostka Serwisowa. Źródło: NASA/Kim Shevlet
Mega księżycowa rakieta Artemis I znajduje się na wyrzutni w[{” attribute=””>NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This powerful Space Launch System (SLS) rocket is getting ready to launch the Orion spacecraft and its European Service Module. The first opportunity for launch is November 16 at 1:04 a.m. EST/local time (07:04 CET, 06:04 GMT).
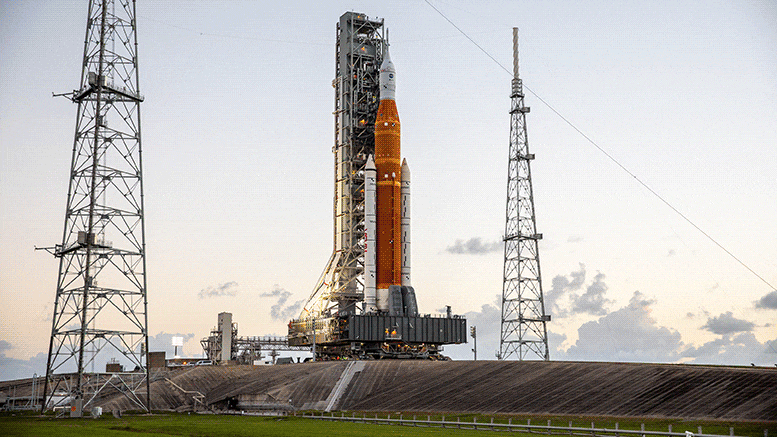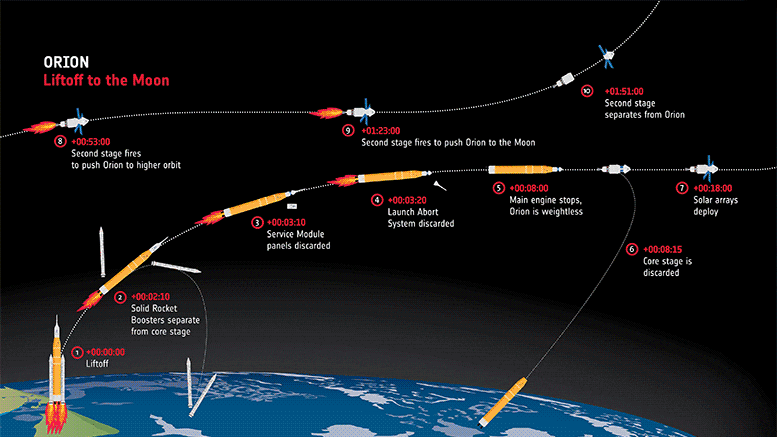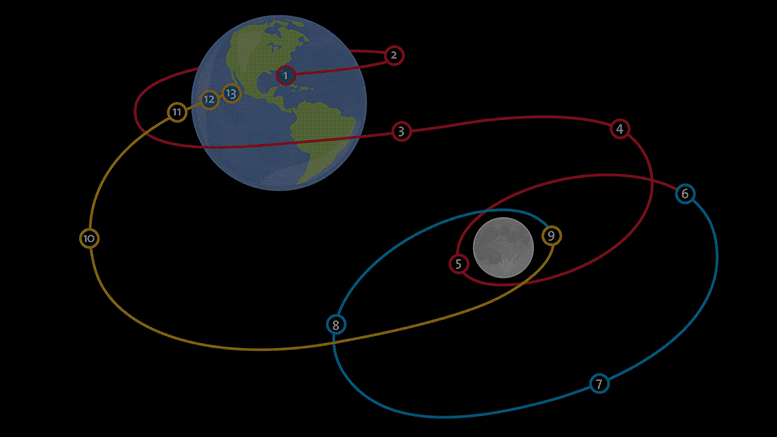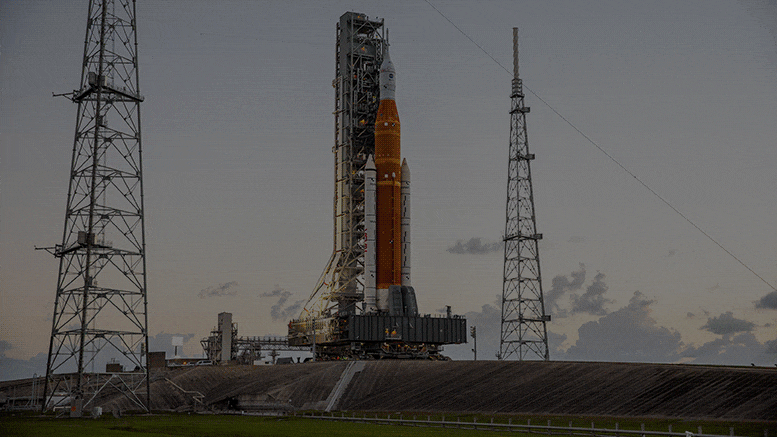
Artemis I is the first mission in a large program to send astronauts around and on the Moon sustainably. This uncrewed first launch will see the Orion spacecraft travel to the Moon, enter an elongated orbit around our satellite, and then return to Earth. The Orion spacecraft is powered by the European-built module that supplies electricity, propulsion, fuel, water, and air in addition to keeping the spacecraft operating at the right temperature.

Artemis I mission overview. Orion is NASA’s next spacecraft to send humans into space and is part of the Artemis program. It is designed to send astronauts farther into space than ever before, beyond the Moon and to the lunar Gateway. Credit: ESA–K. Oldenburg
Artemis to the Moon
The European Service Modules are made from components supplied by over 20 companies in ten European Space Agency (ESA) Member States and the United States. As the first European Service Module sits atop the SLS rocket on the launchpad, the second is only 8 km (5 miles) away, as it is currently being integrated with the Orion crew capsule for the first crewed mission – Artemis II. The third and fourth European Service Modules – that will power astronauts to a Moon landing – are in production in Bremen, Germany.

Contributions in Europe for the European Service Module that is powering the Artemis missions around the Moon. Credit:
ESA–K. Oldenburg
The Artemis program is an international endeavor to build a permanent outpost around and on the Moon. Modules for the lunar Gateway are being built in the United States and Europe, with the first European module – International Habitat – in production in Turin, Italy, and set for launch on the fourth Artemis mission alongside the Orion spacecraft.
The first Artemis launch this week is without humans, but three mannequins have been placed in the spacecraft’s seats to conduct scientific research. Fitted with more than 5600 sensors, two mannequins will measure the amount of radiation astronauts could be exposed to in future missions with unprecedented precision. ESA is also including active radiation dosimeters in the Crew Module to get more data on how radiation levels change on a mission to the Moon – building on the leadership developed over decades of radiation research on the International Space Station.

Logo for the first European Service Module (ESM) that is powering NASA’s Orion spacecraft to send humans into space and the Moon as part of the Artemis program. Credit: ESA
Dates
With a November 16 launch, the three-week Artemis I mission would end on December 11 with a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean. The European Service Module detaches from the Orion Crew Module before splashdown and burns up harmlessly in the atmosphere, its job complete after taking Orion to the Moon and back safely.
Backup Artemis I launch dates include November 19. Watch the launch live on ESA Web TV.
Statek kosmiczny Orion wyposażony w europejski moduł serwisowy będzie latać dalej od Ziemi niż jakikolwiek inny statek kosmiczny sklasyfikowany wcześniej przez człowieka. Ten film przedstawia przegląd pierwszej misji – bez astronautów – Artemidy, ze szczególnym uwzględnieniem Europejskiego Modułu Serwisowego Europejskiej Agencji Kosmicznej, który obsługuje statek kosmiczny. Statek kosmiczny przeleci nad Księżycem, wykorzystując grawitację księżycową, aby nabrać prędkości i rozpędzić się o 70 000 kilometrów od Księżyca, prawie pół miliona kilometrów od Ziemi – dalej niż jakikolwiek człowiek, ponieważ wpompuje się w odległy lot wsteczny. obracać się wokół księżyca. W drodze powrotnej Orion przeleci obok Księżyca przed powrotem na Ziemię. Cała podróż zajmie około 20 dni, a kończy się na wodzie wpadającej do Pacyfiku bez ESU – oddziela się i spala w atmosferze nieszkodliwie. Źródło: ESA – Europejska Agencja Kosmiczna

„Kawioholik. Fanatyk alkoholu na całe życie. Typowy ekspert podróży. Skłonny do napadów apatii. Internetowy pionier”.

/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24054838/AMD_Ryzen_7000_Desktop_CPU_Lineup_low_res_scale_4_00x_Custom.png)




More Stories
Identyczne ślady dinozaurów odkryto na dwóch kontynentach
Studentka Uniwersytetu Północnej Karoliny zostanie najmłodszą kobietą, która przekroczy granice kosmosu na pokładzie Blue Origin
Boeing może nie być w stanie obsługiwać pojazdu Starliner przed zniszczeniem stacji kosmicznej